2.1.9. Retro hunt engine
2.1.9.1. CTI module overview
A database of Indicators Of Compromise named Gatewatcher CTI
The Active CTI engine: it generates Sigflow rules on the basis of the database of Indicators Of Compromise in order to raise alerts
The Retro hunt engine: it searches the Indicators Of Compromise (defined in the database) in metadata (corresponding of the network flow captured by Sigflow)
Note
An additional license is required to activate this module. It is therefore not automatically activated in the solution.
2.1.9.2. Introduction
2.1.9.2.1. For what types of threats is this engine designed?
2.1.9.2.2. How does this particular engine detect threats?
2.1.9.2.3. How does Retro hunt work in the GCenter?
- Hash of a file
- Name of a file
- An IP
- A domain
- A URL
2.1.9.3. Events generated
- In the main interface named WebUI of the GCenter in the
`Alerts`screen:The main interface named WebUI is described in Overview of the WEB UI.
`Retrohunt`engine filter.See the presentation of the WebUI `Alerts` screen.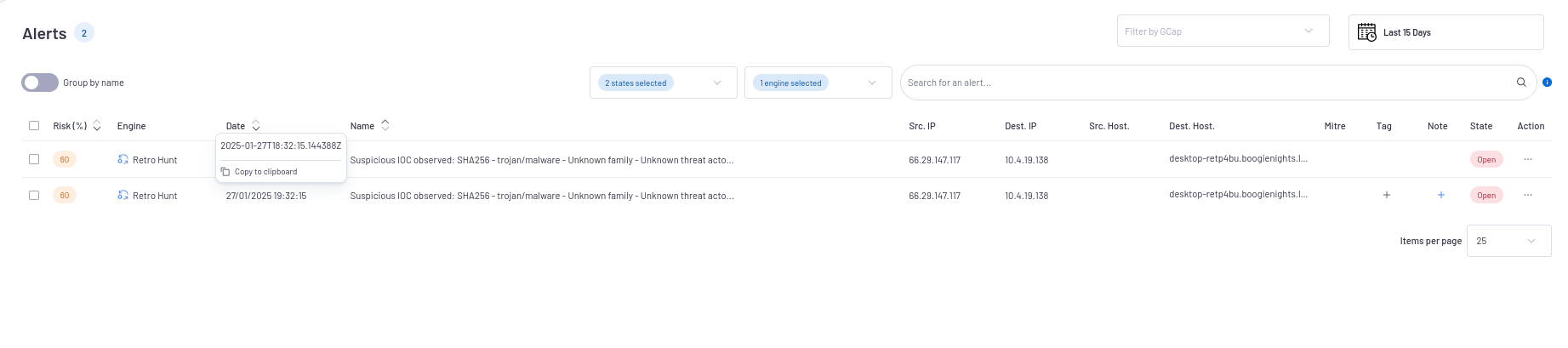
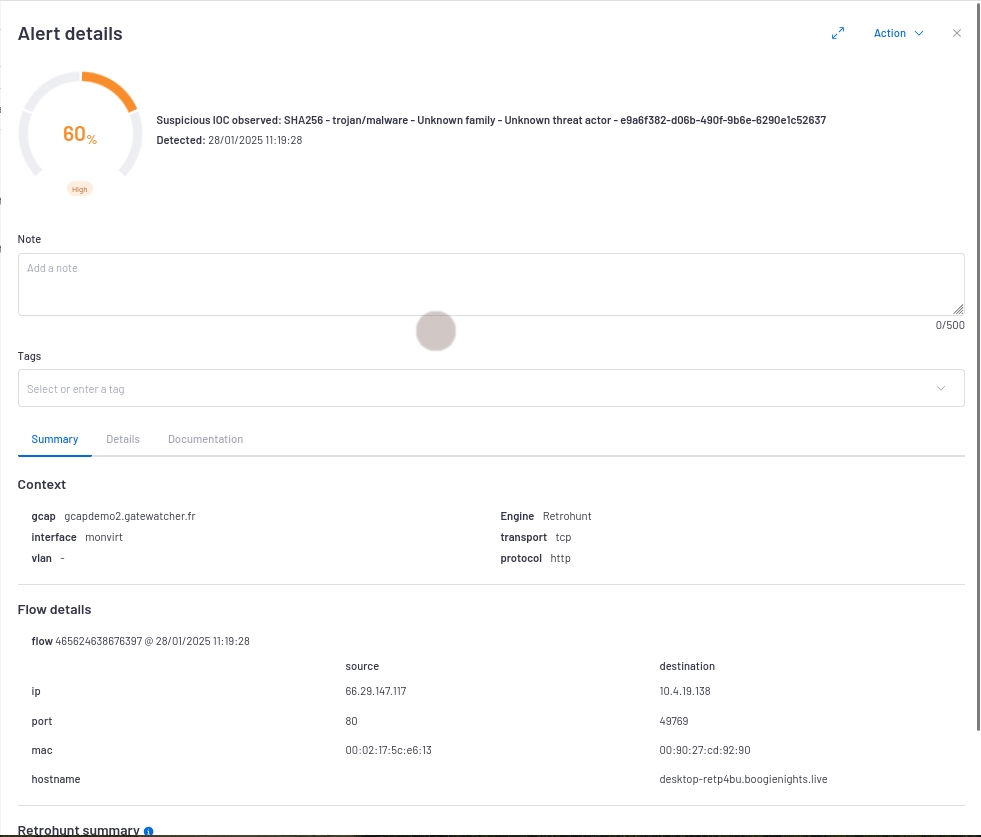
`Alert details`window is displayedThe detailed information of this alert is displayed in Example of a Retro hunt alert in the WebUI.
In the interface named Kibana UI:
- Click on the
`Hunting`icon on the left side menu bar in the WebUI.The interface displayed is the interface named Kibana UI (described in Overview of the Kibana GUI). Select the
`Retro hunt`category of the`Alerts`section in Kibana then the`Overview`or the`Messages`tab.Click on the
`Messages`tab.
To consult information about a specific alert:
- Click on the toggle icon (1) on the left of the Alert.The expanded document (2) is displayed.The detailed information of this alert can be viewed in table or json format (see the Retro hunt logs data structure).The displayed counters are given in the Engine log data structure appendix.
2.1.9.3.1. Example of a Retro hunt alert in the WebUI
`Alert details` window is given in the `Alert details` window.2.1.9.3.2. Retro hunt logs data structure
The logs are composed of different parts:
The header part
The source part defined by "_source"
The field part defined by "_fields"
This information is displayed in the `Expanded document` screen of Kibana.
2.1.9.3.2.1. The header part of Retro hunt logs
The header section contains:
"_index": "engines_alerts",
"_id": "-",
"_version": 1,
"_score": 0,
The detailed information is given in the table (Counters of the header part of logs).
2.1.9.3.2.2. The source part of Retro hunt logs
The source part is defined by "_source" in the logs.
Note
`Extended document` screen on the Kibana interface.The example given here is a Kibana example.
The source part defined by "_source" contains:
"event": {
"kind": "alert",
"module": "retrohunt",
"dataset": "alert",
"created": "2025-01-28T13:03:18.957749+00:00",
"category": [
"network",
"intrusion_detection"
],
"severity_human": "Suspicious",
"id": "0af24ad7-2b4f-4dae-999f-7b2b5737f69c",
"severity": 3
},
"network": {
"transport": "tcp",
"protocol": "http",
"timestamp": "2025-01-28T10:19:28.070435+00:00",
"flow_id": 465624638676397
},
"source": {
"port": 80,
"ip": "x.y.z.A",
"mac": "02:04:c8:5c:e6:13"
},
"matched_event": {
"content": {
"event": {
"kind": "event",
"module": "sigflow_file",
"dataset": "network_metadata",
"created": "2025-01-28T10:19:28.070435+0000",
"category": [
"network",
"file"
],
"id": "e997dbcb-5432-4f53-af03-447a6ea7debc"
},
"network": {
"transport": "tcp",
"protocol": "http",
"timestamp": "2025-01-28T10:19:28.070435+0000",
"flow_id": 465624638676397
},
"source": {
"port": 80,
"ip": "x.y.z.A",
"mac": "02:04:c8:5c:e6:13"
},
"user_agent": {
"original": "Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 10.0; Win64; x64) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/112.0.0.0 Safari/537.36 Edg/112.0.1722.48"
},
"file": {
"magic": "Zip archive data, at least v2.0 to extract",
"file_id": 43,
"sid": [
1100083
],
"name": "643d0491bcea1.zip",
"tx_id": 0,
"state": "CLOSED",
"stored": true,
"gaps": false,
"hash": {
"md5": "b054104df97949cbeb3da2290da0cf40",
"sha256": "eb4db357dc6f2dd8facf132ecaf6916e7219bf0e29990601b1f4babefa4d02f9"
},
"size": 5665
},
"observer": {
"log_format_version": "1.0.0",
"hostname": "gcenter.gatewatcher.fr",
"version": "2.5.3.103",
"gcap": {
"hostname": "gcap.gatewatcher.fr",
"version": "2.5.4.0-rc9",
"ingress": {
"interface": {
"name": "monvirt"
}
}
},
"uuid": "27863930-fab5-5abe-ba40-1fbd5481e9a4",
"product": "gcenter",
"vendor": "gatewatcher"
},
"metadata": {
"flowbits": [
"et.http.PK"
]
},
"destination": {
"port": 49769,
"ip": "x.y.z.a",
"mac": "00:90:27:cd:92:90"
},
"ecs": {
"version": "8.6.0"
},
"url": {
"domain": "cotecsecuritygroup.com",
"path": "/wicd/643d0491bcea1.zip"
},
"http": {
"response": {
"status": 200,
"bytes": 5673,
"mime_type": "application/zip"
},
"hostname": "cotecsecuritygroup.com",
"version": "HTTP/1.1",
"request": {
"method": "GET"
}
}
},
"id": "e997dbcb-5432-4f53-af03-447a6ea7debc"
},
"ioc": {
"case_id": "aa8d51ed-0883-4b12-8b43-4b285306b0a6",
"type": "SHA256",
"threat_actor": [],
"updated_date": "2025-01-28T08:04:31+00:00",
"categories": [
"trojan",
"malware"
],
"signature": "SHA256 - trojan/malware - Unknown family - Unknown threat actor - e9a6f382-d06b-490f-9b6e-6290e1c52637",
"creation_date": "2025-01-28T08:02:50+00:00",
"targeted_platforms": [],
"external_links": [
{
"url": "https://info.gatewatcher.com/fr/speed-meeting-lastinfosec",
"source_name": "IOCAnalysisCollector"
}
],
"vulnerabilities": [],
"relations": [
"0e3cc27b-7999-48ce-8484-dc12b325a355",
"5556c4ab-3e5e-4d56-8410-60b29cecbeb6"
],
"targeted_organizations": [],
"families": [],
"tags": [
"trojan.generickd.66527077",
"troj/drodzp-cf",
"trojan.generickd.66527077 (b)",
"trojan/generickd!vemnohoo"
],
"targeted_sectors": [
"Services - Autres"
],
"description": "'eb4db357dc6f2dd8facf132ecaf6916e7219bf0e29990601b1f4babefa4d02f9' is a Suspicious SHA256.\nThis SHA256 is linked to a trojan attack.\nWe advised to use this IoC in detection mode.",
"ttp": [],
"usage_mode": "detection",
"tlp": "green",
"campaigns": [],
"targeted_countries": [],
"meta_data": {
"descriptions": [],
"usageMode": "detection",
"cwe": []
},
"value": "eb4db357dc6f2dd8facf132ecaf6916e7219bf0e29990601b1f4babefa4d02f9",
"kill_chain_phases": [],
"id": "e9a6f382-d06b-490f-9b6e-6290e1c52637",
"package_date": "2025-01-28T08:50:04.124404+00:00"
},
"observer": {
"log_format_version": "1.0.0",
"hostname": "gcenter.gatewatcher.fr",
"version": "2.5.3.103",
"gcap": {
"hostname": "gcap.gatewatcher.fr",
"version": "2.5.4.0-rc9",
"ingress": {
"interface": {
"name": "monvirt"
}
}
},
"uuid": "27863930-fab5-5abe-ba40-1fbd5481e9a4",
"product": "gcenter",
"vendor": "gatewatcher"
},
"destination": {
"port": 49769,
"ip": "x.y.z.a",
"mac": "00:90:27:cd:92:90"
},
"@timestamp": "2025-01-28T13:03:18.957Z",
"ecs": {
"version": "8.6.0"
},
"@version": "1"
2.1.9.3.2.3. List of counters of the alert
Note
The alert counters are visible:
In the
`Alert details`screen of the WebUIIn the
`Expanded document`screen of KibanaIn the export to the SIEM
The detailed information is given in the table (Counters of the source part of logs).
2.1.9.4. Management of the engine
2.1.9.4.1. Viewing the engine status
The current engine status is displayed in the `Health checks` screen.